4 Areas of Artificial Intelligence
Megan Mocko & Alexandra Bitton-Bailey, Ph.D.

Machine Learning is a “method of data analysis that automates analytical model building. It is a branch of artificial intelligence based on the idea that systems can learn from data, identify patterns and make decisions with minimal human intervention.” Machine learning is a process in which the computer can predict or classify without being given explicit information on exactly how to make that decision. The computer uses the data to help it determine the prediction or decision. Arthur Samuel is believed to have coined the expression “machine learning” while working on the game of checkers. In 1962 the checkers expert Robert Nealey played checkers with and lost to a computer.
There are many subfields of machine learning, including deep learning. Deep learning is a subfield of machine learning. It is considered “an evolution of machine learning that uses programmable neural networks that enables machines to make accurate decisions without help from humans.” In 2020, IBM Cloud Education presented a non-technical explanation of deep learning and gave applications. Machine learning has numerous subcategories, including speech recognition and computer vision.
Speech recognition, also known as computer speech recognition, automatic speech recognition, or speech-to-text, is a subfield of computer science and computational linguistic. It allows a program to process human speech to complete tasks such as generating speech to text, translating languages, navigating a location using a vehicle’s global positioning system (GPS), finding a recipe, and operating appliances. Speech recognition includes speech synthesis and semantic understanding, which uses neural networks to extract meaning from speech.
Computer vision allows computers to interpret and understand (i.e., see) the visual world. Computers do this by using digital images and machine learning to classify objects. For example, computer vision can analyze medical images for more accurate diagnosis, process and analyze live-action sports, solve crimes through facial detection and recognition, and scan documents to extract essential information.
Neural Networks, also called artificial neural networks or neural nets, “is a computational learning system that uses a network of functions to understand and translate a data input of one form into a desired output, usually in another form. “A neural network takes data as an input and passes it through algorithms to make either a classification or a prediction. These algorithms are not interpretable and are often called the hidden layer. IBM cloud education explains that “artificial neural networks are comprised of a node layers comprised of a node layers, containing an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. Each node, or artificial neuron, connects to another and has an associated weight and threshold. If the output of any individual node is above the specified threshold value, that node is activated, sending data to the next layer of the network. Otherwise, no data is passed along to the next layer of the network.”
Neural networks must be trained on data to achieve any level of accuracy. This is done over time. Once the learning algorithms are fully functional neural networks can classify and cluster data in a powerful way.
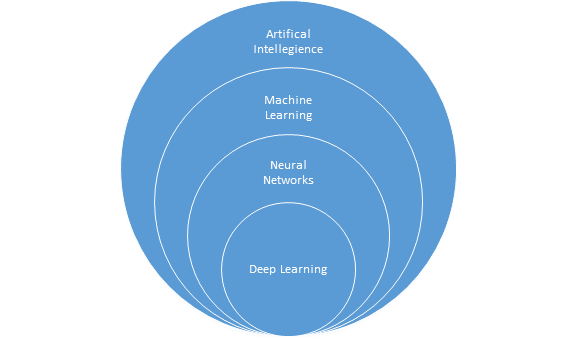
Figure 1: The relationship between A.I., Machine Learning, Neural Networks and Deep Learning.
Natural language processing (NLP) combines linguistic, machine learning, and statistical and deep learning models. NLP allows machines to understand and respond to text or voice similar to how humans do. Current uses of NLP include translating languages, retrieving information, analyzing sentiments from social media posts, proofreading documents for errors, and providing customer service. Though this may sound simple, NLP is ambiguous and complex, and relies on contexts and situations. It is also fraught with complexities and is quite ambiguous.
Expert Systems are computer systems that are designed to solve complex problems and mimic the decision-making process of a human expert in a given field. These systems make decisions using extensive data and if-then rules rather than procedural codes. Expert systems are entirely reliant on the expert knowledge accumulated in the knowledge base and are known to be highly responsive and reliable.
Fuzzy logic is an approach to computing that is based on “degrees of truth” rather than the typical true-false approach. It allows computers to account for the uncertainty that humans encounter in the real world and measures the degree to which the hypothesis is correct.

Robotics is the interdisciplinary field of computer science, mechanical and electrical, and other disciplines to create machines called robots. A few decades ago, robots consisted mainly of mechanical arms that performed tasks in manufacturing industries (e.g., lines) that would be overly laborious for humans to perform consistently and in an ongoing fashion. While robots are still used primarily to perform these vital tasks, there is now an evolved and expanded definition of robotics. Robots and bots are now used in fields such as healthcare, law enforcement, and space exploration.

Feedback/Errata