Modules – Skills & Tools
Molecular Diagnostics – Bioinformatics
Background Information
Molecular diagnostics is a transformative field in microbiology that enables the detection, identification, and study of microorganisms at the molecular level. Techniques like PCR are central to this field, allowing for the amplification and analysis of specific DNA sequences. These methods are underpinned by the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein. The analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences is a key application, facilitating the identification and comparison of microbial species.
Modern molecular diagnostics also benefits from tools derived from naturally occurring microbes, such as cloning vectors, restriction enzymes, and CRISPR/Cas systems. These innovations have revolutionized research and diagnostic practices, leading to advancements in personalized medicine, agricultural biotechnology, and emerging technologies like the aforementioned CRISPR/Cas systems for disease surveillance. Molecular diagnostics is not just essential for detecting and identifying microbes but also a cornerstone technique for advancing various fields of science and medicine.
Learning Objectives:
After completing this module, students will be able to:
- Recall new vocabulary, definitions and processes that pertain to this module.
- Use appropriate methods to identify microorganisms on a molecular level using PCR.
- Use appropriate microbiological and molecular lab equipment and methods: PCR Machine, spectrophotometer, gel electrophoresis and gel imager.
- Explain the central dogma of molecular biology and explain how it relates to this experiment.
- Recall how to retrieve 16s rRNA data for microbes (NCBI).
- Discuss the benefits of using tools of modern biotechnology that are derived from naturally occurring microbes (e.g. cloning vectors, restriction enzymes, Taq polymerase, etc.).
Access OpenStax: Ch. 12 Introduction, 12.1 Microbes and the Tools of Genetic Engineering, and 12.3 Whole Genome Methods and Pharmaceutical Applications of Genetic Engineering
History Connections
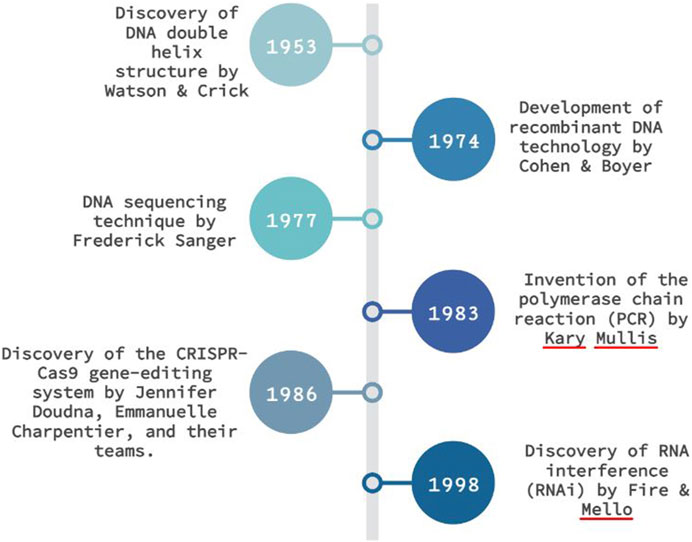
The history connection of molecular diagnostics is extensive and includes:
- Watson and Crick described of the molecular structure of DNA in the 1950ies (Nobel prize in Physiology or Medicine for Crick, Watson and Wilkins in 1962)
- Discovery of thermophile bacterium Thermus aquaticus in the 1960ies in Yellowstone (Note: Thermus is an extremophile but not an archaebacterium, the enzyme Taq polymerase used for PCR)
- Sanger developed a method to map and sequence DNA in 1977 (Nobel Prize in Chemistry for Fredrick Sanger in 1980)
- Mullis developed a method to amplify DNA, the Polymerase Chain Reaction in 1983 (Nobel Prize in Chemistry for Kary Mullis in 1993, shared with Michael Smith for site directed mutagenesis)
- Woese uncovered the third domain of life, proposed the classification of Archaea, (Eu)Bacteria and Eucarya in 1977, using 16s rRNA PCR he established the new domain of Archaebacteria and also developed rRNA as “molecular chonometer”, the molecular marker to develop a tree of life. Watch this short documentary on his discovery
- Sequencing of the first whole genome from Haemophilus influenzae in 1995 with a genome of 1,830,140 base pairs of DNA.
- The first human microbiome was sequenced based on 16s rRNA in 1996, although research in the field date back to Leeuwenhoeck and Escherich (2). Check out the Milestones in human microbiota research.
- The Human Genome project published a first version of the Human Genome in 2004 with a genome of about 3.1 billion base pairs
- Two women, Charpentier and Dounda developed a method for genome editing, called CRISPR/CAS9 first described in the early 2000s (Nobel Prize in Chemistry for Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Dounda in 2020)
This is a small snapshot of some of the key events in the history of molecular diagnosis.
Virtual Lab Simulation
Gel Electrophoresis Virtual Lab Simulation:
For this online lab, you will be completing both of the virtual lab simulations provided in the module (PCR & Gel electrophoresis). In your ELN, just describe the procedures of both activities and their real-world applications. For data, screenshot pictures of the activities (with identification present), and describe their relevance in the results.
Online Lab
Pipetting activity
If you have not yet done the pipetting activity using your silica gel during the earlier chapter, please practice pipetting with your model gel.
Submit a photo of your loaded gel in your ELN.
Bioinformatics activities
Please complete the activities in the bioinformatics modules. Videos are provided for the activities
As much as possible try to find a gene, protein or plasmid that relates to your “Adopt a microbe” organism. Retrieve the sequences through NCBI (Obtaining sequence from NCBI (video)) and use those for the different bioinformatics activities.
For your ELN submit screenshots of the different activities. Pick 7 activities of your choice, explain in your own words the purpose of the program and interpret the results.
In-Person Lab
Activity: Molecular Diagnostics
Bioinformatics activities
Please complete the activities in the bioinformatics modules. Videos are provided for the activities
Activity: MiniPCR and BlueGel Use & Application
Resources
Take a look at the appropriate module for the vocabulary that is being tested: Microbiology @ UF Lab Terminology Quizlet
LINKS
- Design primers for a given DNA sequence using Primer3Plus.
- Video tutorial for designing ‘cloning’ primers using Primer3Plus.
- Know how to calculate the melting temperature (Tm) of a primer
- count all As and Ts and multiply by 2, count all Gs and Cs and multiply by 4, add both numbers
- (A/T x 2) + (C/C x 4) = Tm
- and check out the Tm calculation software Primer Tm
- count all As and Ts and multiply by 2, count all Gs and Cs and multiply by 4, add both numbers
- Methods and primers for 16s rRNA can be found in the JOVE protocol (need VPN)
- “Run” a PCR reaction selecting specific organisms and using specific primers In silico PCR – identify the sequence
- Understand and explain DNA extraction, PCR, gel electrophoresis (Genetics for classroom virtual lab) and Sanger sequencing
- Know how to make a PCR MasterMix from scratch (you can use the PCR Master Mix calculator.)
- Suspend and calculate primer concentration: Primer order sheet molecular primer sheet-1.pdf
- Make a PCR master mix using GoTaq Hot Start master mix
- Understand how this process work in the in person microbiology lab
- DNA extraction, purification and concentration determination https://vimeo.com/49327264
- PCR, gel electrophoresis and gel imaging https://vimeo.com/49520521
- PCR product purification https://vimeo.com/49520034
- MiniPCR Resources and tutorials https://www.minipcr.com/videos/